Microshocks
Sometimes, when someone is walking or cycling under an overhead line, they may experience a small spark, or microshock, when touching other objects. These are quite rare and depend on a number of factors including clothing and the weather. The same person could walk under an overhead line many times without experiencing a microshock, but sometimes the conditions are such that one may occur. Although initially the spark can seem concerning, there are no health effects associated with these, and they are similar to receiving a static shock like you may get from a car door or trampoline.
This page explains what microshocks are, the factors which effect their likelihood, and how to prevent them.
What causes a microshock?
A microshock happens when a person and a conducting object acquire different potentials in an electric field. At the instant of coming into contact, the two potentials are equalised by a transfer of charge, and that momentary transfer of charge, concentrated at a single point on the skin, constitutes a microshock.
This can happen two different ways. In both cases, the common feature is the person touching an object, where one is at earth potential (no charges accumulated on it) and the other, which is not earthed, has been raised to a higher potential by the electric field (charges accumulated on it). When the person touches the object, charge flows so as to equalise the potentials, and this charge, concentrated on the small area of skin where contact is first made, creates the microshock.
The left-hand side of the diagram shows a person who is grounded through their feet and then touches an ungrounded object. The right-hand side shows a person who is isolated from ground (because they are wearing insulating footwear or are standing on an insulating surface) and then touches a grounded conducting object.
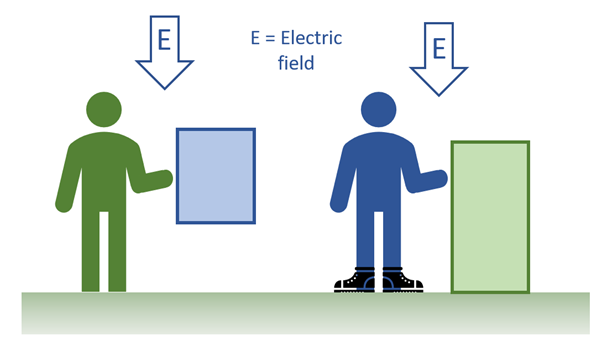
What factors affect a microshock being perceived?
Under an overhead line, different objects have different charges induced on them, and the size of these charges is important. So, what determines how likely we are to receive a microshock?
- The electric field: as the field increases, so does the likelihood of perception.
- The capacitance between the two objects: capacitance determines how well the charge will flow between the two objects. The size and proximity of the objects determines how much they are electrically linked before the discharge.
- Atmospheric conditions: perception is more likely in dry, hot weather.
- Footwear and clothing: insulating footwear can cause a greater build-up of charge.
- Size of the objects: the larger the unearthed object, the greater the charge it can accumulate.
What measures are in place in the UK to control microshocks?
The ICNIRP exposure limits that control exposures to EMFs sometimes mention indirect effects, including microshocks, but usually only in general terms.
More detailed guidance for the UK is contained in a Code of Practice adopted in 2013 by the Government’s Department for Energy and Climate Change (now the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero) and industry (the Energy Networks Association).
Two of the key statements are:
"This Code of Practice recognises that there is no reasonable way to avoid microshocks in all circumstances, even in circumstances when they are at a frequency and severity that is clearly undesirable, and therefore that not all situations producing microshocks are expected to be remedied."
and
"This Code of Practice also recognises that control of microshocks is not based on a simple quantitative limit. Rather, there is a suite of measures that may be called upon in particular situations."
It then outlines the "suite of measures" that should be called upon, summarised as follows:
- Electricity companies will, where reasonably practicable, avoid designing new power lines that would create fields of 5 kV/m or greater in homes, other land in residential use, their curtilage, and schools.
- Electricity companies will continue to make information available to the public about microshocks. They will seek appropriate ways to communicate to specific communities affected (e.g., cyclists and horse-riders).
- When an electricity company becomes aware that a particular situation is giving rise to microshocks in a persistent and annoying manner:
- The company will offer focused advice and information specific to the situation;
- Where earthing is an easy solution, this is encouraged, and will be explained to the landowner or occupier by the electricity company;
- Where microshocks occur in someone’s garden, or in other circumstances where one individual could be exposed to multiple shocks over a prolonged period, every reasonable effort will be made by the electricity company to develop solutions by earthing, by changing a conducting object to an insulating one, by use of appropriate clothing, or by screening structures or trees and vegetation; and
- Where a site-specific risk analysis indicates a significant risk of injury (assessed using normal health and safety practice) from startle reactions to a microshock, mitigation measures, potentially including screening structures, will be developed by the electricity company, and, to the extent that it lies within the company’s control, deployed, if this can be done without becoming unreasonable.
Note that these are edited summaries. See the Code of Practice for the full wording and for additional explanatory material.
If you experience a microshock under an overhead line and would like to discuss this, please contact our public helpline. The details are at the bottom of every page.