Current research on health
At high levels of EMF exposure, there are several established effects, including induced currents, microshocks, and effects on equipment. Because they are well researched and established, there are measures in place to protect against these effects; mainly exposure limits.
This page addresses the possibility of effects at lower levels. These are effects which are not established, but where there has been research investigating if they could occur at EMF levels below the exposure limits, at the levels of exposure an overhead line or substation may produce.
These potential effects have been the subject of a vast amount of research, carried out over the past 40 years. This research has not established any health effects at levels below the guidelines. However, there is one area where some uncertainty exists and that’s around childhood leukaemia.
Childhood leukaemia
Of all the possible effects of EMFs, the main concern is around childhood leukaemia.
The uncertainty comes from an area of science called epidemiology, which looks for statistical patterns in diseases. This type of study can only find associations, not causes of diseases. Two of the most notable epidemiological studies to find associations between EMFs and childhood leukaemia were published in the early 2000s. These found children who were exposed to prolonged higher levels of magnetic fields or those born within 200 m of a high voltage overhead line (400 kV or 275 kV) had a higher risk of leukaemia. Since those studies were published, many of the most recent studies have shown much weaker associations, with some finding no increased risk of childhood leukaemia at all. In addition to these statistical studies, a vast number of laboratory studies have looked to see if and how magnetic fields could cause childhood leukaemia. These laboratory studies show no increased cases of leukaemia in animals and provide no evidence of how magnetic fields could cause childhood leukaemia. Therefore, the uncertainty is a weak statistical association only, with no evidence for causation.
Whilst the epidemiological evidence for childhood leukaemia has become weaker in the last two decades, the guidelines and precautionary measures that are in place in the UK have been developed with acknowledgement of this uncertainty. Based on the evidence, the UK has a carefully thought-out set of policies for protecting against EMFs. This includes both numerical exposure guidelines to protect against known established effects of EMFs, and precautionary policies to provide appropriate protection against the possibility of a risk of childhood leukaemia at lower levels of EMFs.
All overhead lines, underground cables, and substations are designed to comply with these guidelines and policies which have been set to protect us all against EMFs.
Other human health effects
The evidence for EMFs causing other health effects is weaker than that discussed above for childhood leukaemia. This section summarises the evidence for the other health effects which have been investigated.
An overall comment on health effects other than childhood leukaemia comes from the World Health Organistation's (WHO) monograph:
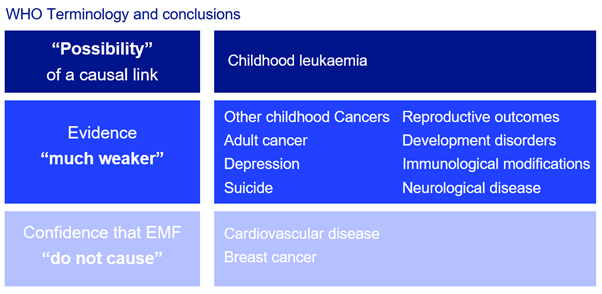
"The scientific evidence supporting a linkage between ELF (extremely low frequency) magnetic fields and any of these diseases is much weaker than for childhood leukaemia and in some cases (for example, for cardiovascular disease or breast cancer) the evidence is sufficient to give confidence that magnetic fields do not cause the disease." and we summarise it here: other cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, suicide and depression, and many others.”
Below is the WHO's summary of research into different health outcomes and how they rank that evidence.